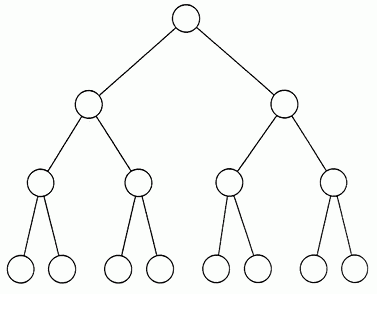
The Document Object Model (or DOM for short) is the main structure under which HTML operates; it can be conceptualized as interconnected nodes arranged via a tree-like structure. The archetypal method through which these nodes may be traversed relies upon recursion.
An easy way picturing this is to imagine a single node carrying some number of child-nodes. Those aforementioned child-nodes might carry child-nodes of their own, and so on and so forth. In this way, we are able to conjure an image of a tree.
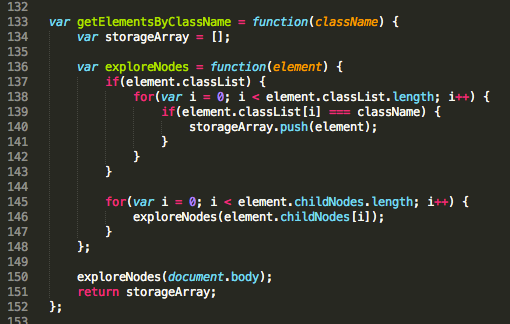
The code snippet as shown below is one example of how one might manage to interact and traverse between the DOM nodes. The function getElementsByClassName collects every element of the DOM that carries a class name equivalent to the one searched for by the programmer. It then returns those elements within an array once the entire DOM has been searched.